Unreal Engine Pixel Streaming: Your Complete Guide
- Shrenik Jain
- Jun 21, 2025
- 12 min read
Understanding Pixel Streaming: What It Really Means

This technology fundamentally changes how we access high-quality digital experiences. It removes the barriers that have historically limited who can engage with detailed 3D content. Access is no longer restricted to people with expensive gaming PCs or specialized workstations. Anyone with a modern web browser and a stable internet connection can now participate. This opens the door for universally accessible product configurators, architectural visualizations, and complex training simulations.
The Core Concept: Remote Rendering
At its heart, pixel streaming is a form of remote rendering. The Unreal Engine application runs on a high-performance computer in a data center, not on your local machine. This server renders each frame of the 3D scene in real-time, compresses it into a video, and streams it across the web to your browser.
Here’s how it differs from the old way:
Traditional Method: Your computer's GPU and CPU must process the 3D models, textures, and lighting. This requires significant local processing power, and the quality is limited by your hardware.
Pixel Streaming Method: A remote server with a top-tier GPU manages all the rendering. Your device only needs to decode a video stream, a task most modern smartphones and laptops can do easily.
This difference is key. It separates the quality of the visual experience from the power of the end-user's device. A user on a budget tablet can have the exact same immersive experience as someone on a high-end desktop because they are both watching a video stream from the same powerful source.
Why This Matters Now
The use of real-time 3D technology is growing quickly, and Unreal Engine pixel streaming is a major part of this shift. In 2022, the engine's monthly active users grew by an average of 23% globally. This growth was especially strong in North America, with a nearly 40% increase, showing a massive demand for interactive content. With 73% of users moving to Unreal Engine 5 since its release, the advanced features that support high-quality streaming are more common than ever. To learn more about these trends, you can read the full report on the state of interactive 3D.
This growing ecosystem means more developers are creating experiences designed for streaming, making it easier for businesses to adopt these solutions. The choice between a fully managed service and a self-hosted setup depends on your team's technical skills and project needs. You can check out our guide on self-hosted vs. managed pixel streaming to figure out the best path for you. The technology has matured, making it a practical and effective tool for a wide range of industries.
The Magic Behind The Streams: How It Actually Works
To really get a feel for what makes Unreal Engine pixel streaming so powerful, it helps to peek behind the curtain at the technical dance happening in the background. When you interact with a streamed application, you’re not just clicking on a simple video. You're connecting to a complex, well-orchestrated system.
Imagine a high-performance computer running your 3D application in the cloud. This server is doing all the heavy lifting—rendering every frame, compressing it into a high-quality video, and sending it to your screen almost instantly. This process creates a fluid, interactive experience on your device, no matter how powerful it is. Let's break down the components that make this possible.
The Core Technical Pipeline
The whole system works like a continuous loop. The server renders the scene, encodes it into video, and streams it to you. At the same time, your device sends your mouse clicks and keyboard inputs back to the server. This cycle repeats many times per second, making it feel like the application is running right on your own machine.
The diagram below shows the basic setup, illustrating how the demanding work is handled by the server, leaving your device to simply display the video and capture your actions.
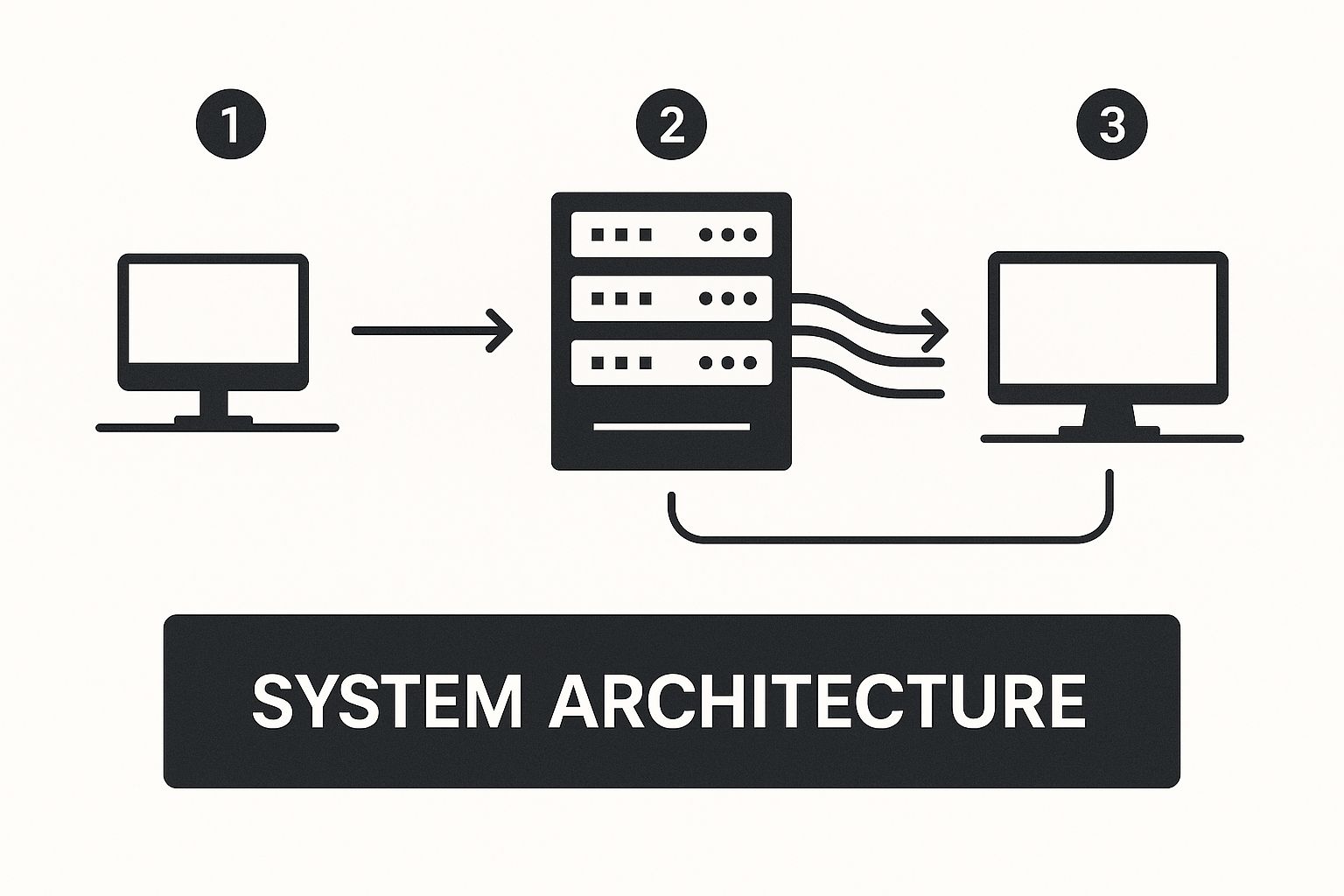
This setup is key to pixel streaming's efficiency. By offloading the rendering, even a smartphone can run a graphically intense application that would normally require a high-end gaming PC.
Here’s a step-by-step look at how the process unfolds:
Server-Side Rendering: An Unreal Engine application runs on a cloud server with a powerful GPU. It renders the 3D world at a high frame rate, just like it would on a desktop computer.
Frame Capture and Encoding: Every rendered frame is immediately captured and passed to a video encoder. This encoder uses a codec (like H.264) to compress the frame into a video stream, making it small enough to send over the internet quickly.
Network Transmission: The compressed video is sent to your device using WebRTC, a technology built for real-time video and audio communication. WebRTC is designed to minimize latency—the delay between your action and the result you see on screen.
Client-Side Decoding: Your web browser receives and decodes the video stream, displaying the frames as they arrive. This requires very little processing power from your device.
User Input Handling: When you click, type, or touch the screen, your browser captures these actions and sends them straight back to the server. The server feeds these inputs into the Unreal Engine application, which updates the scene, renders a new frame, and starts the cycle all over again.
Signaling and Connection
Before any streaming can begin, your browser needs to find and connect to the right application server. This is where a Signaling Server comes in. Think of it as a digital matchmaker. It introduces your browser (the client) to the specific Unreal Engine application instance (the server) you need to connect to.
Once the introduction is made, the Signaling Server steps aside, and a direct line of communication is established for video and input data. The system is also smart enough to adjust the video quality automatically based on your network speed, ensuring the experience stays as smooth as possible.
Game-Changing Benefits That Transform Possibilities
Adopting Unreal Engine pixel streaming does more than just solve technical problems; it opens up entirely new ways for people to interact with your content and for your business to operate. The most powerful benefit is making high-end graphics available to everyone. Suddenly, the hardware barrier disappears. A user with a basic smartphone can explore a photorealistic 3D world that would normally demand a powerful, expensive computer. This instantly expands your potential audience.
This technology also smooths out the user experience by removing common obstacles. There are no downloads, no installations, and no compatibility checks. A customer can jump directly into a complex application, like an architectural walkthrough or a product configurator, just by clicking a web link. This instant access dramatically improves engagement and cuts down on the need for technical support for installation issues.
Accessibility and Scalability on a Global Scale
One of the most impressive aspects of pixel streaming is its ability to scale. Unlike technologies such as WebGL that rely on the user's hardware to render graphics, pixel streaming does all the heavy lifting in the cloud. It then streams the result as a crisp video, letting even low-spec devices run demanding 3D applications in real time. This ensures a consistent, high-quality experience for everyone, no matter what device they use.
This centralized model also makes operations much simpler. Updates are applied just once on the server, and every user immediately gets the newest version. This gets rid of version control headaches and makes sure all stakeholders are always looking at the most current project iteration.
Security and New User Experiences
Security is another significant advantage. Because the 3D assets and core application logic never leave the secure cloud server, your intellectual property stays protected. Users only get a video stream, making it impossible for them to reverse-engineer or tamper with the underlying files. This is especially crucial for industries with valuable proprietary designs, such as automotive or aerospace.
By combining these benefits, pixel streaming makes entirely new kinds of interactive experiences practical for the first time. The key advantages include:
Universal Access: Reach users on any device with a modern web browser, from desktops to tablets and smartphones.
Zero Installation: Give users immediate access to your application, which drastically reduces drop-off rates.
Centralized Management: Simplify updates and maintenance by managing a single server-side application.
Enhanced Security: Keep your valuable 3D models and proprietary code safe in the cloud.
Consistent Quality: Deliver a high-fidelity visual experience to every user, independent of their hardware.
Delivering these high-quality streams consistently depends on optimizing the application itself. To get the best results, you should check out our guide on how to improve pixel streaming performance with Unreal Engine 5 best practices.
Real Industries, Real Solutions: Where It's Working
The theory behind Unreal Engine Pixel Streaming is interesting, but its true power comes to light when you see it solving real problems in different industries. It’s not just a niche tool for tech companies; it’s a practical solution that changes how businesses connect with their audiences by delivering complex visual experiences without a hitch. From digital car showrooms to advanced medical training, the applications are as varied as they are powerful.
The core idea is simple: remove the hardware barrier. A potential car buyer doesn't need a high-end gaming PC to customize their dream vehicle; they can do it on a tablet. An architect can walk a client through a photorealistic building from halfway across the world. By streaming the experience, high-fidelity 3D content becomes universally accessible, giving businesses a distinct advantage.
Automotive Configurators
The automotive industry was one of the first to fully embrace pixel streaming, using it to build incredible online showrooms. Instead of flipping through a gallery of static images, customers can now interact with a lifelike digital twin of a vehicle in real-time.
Here’s why it works so well:
Unmatched Detail and Realism: Users can cycle through paint colors, test different interior materials, and swap out wheel designs, seeing every change instantly in photorealistic quality.
Access from Anywhere: These configurators run directly in a web browser on any device, meaning customers don’t have to visit a dealership just to see their options.
A Powerful Sales Tool: This deep level of engagement often shortens the sales cycle. Customers can build and save their perfect car before they even speak to a sales representative.
This direct, hands-on interaction creates a strong emotional connection to the product, making a sale more likely long before a test drive even happens.
Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC)
For architects, engineers, and construction firms, pixel streaming is a game-changer for communicating design ideas. It turns complicated blueprints and 3D models into interactive, explorable spaces that clients can easily understand.
Imagine a group of stakeholders, all in different cities, taking a virtual walkthrough of a new building together. They can spot potential issues, discuss changes, and make decisions on the fly. This collaborative process speeds up approvals dramatically and helps avoid expensive mistakes during the actual construction phase.
To give you a clearer picture of its impact, the table below breaks down how various industries are applying pixel streaming to solve specific challenges.
Pixel Streaming Applications by Industry
Comparison of how different industries implement pixel streaming solutions, including use cases, benefits, and typical user scenarios
As the table shows, the core benefit is always about making complex visual information accessible and interactive. Whether it's training a surgeon on a new procedure or letting a fan explore a virtual movie set, pixel streaming closes the gap between the digital world and the end-user, no matter what device they're on.
Infrastructure Reality Check: What You Actually Need

The core of any pixel streaming setup is the server-side hardware, especially the GPU, which does all the heavy graphical work. For every person using your application at the same time, you need a dedicated GPU instance powerful enough to render your scene at the desired quality. A high-end GPU, like an NVIDIA RTX 6000, can be divided to serve multiple users, but this demands careful management to prevent performance from dropping. This direct relationship between a user and a GPU slice is a major factor in both cost and capacity planning.
The Cloud vs. On-Premise Debate
The next big choice is where to house your hardware. Running your own servers on-premise gives you complete control, but it also means a big upfront investment, ongoing maintenance, and needing physical space. For most, the cloud is a more sensible path, offering the ability to scale up or down as needed. However, not all cloud services are created equal. While major providers offer GPU instances, you have to consider:
Variable Costs: Pricing models can be tricky, with separate fees for processing time, data transfer, and storage.
Instance Availability: In-demand GPU instances can be scarce in certain regions, which can stop you from scaling when you need to.
Network Performance: Latency is everything. The physical distance between your users and the data center has a direct effect on how responsive the stream feels.
This is why specialized platforms like Streampixel, which are built specifically for this purpose, can provide a more reliable and optimized environment for Unreal Engine pixel streaming.
Making It Work: Strategic Implementation Approaches
Taking an Unreal Engine pixel streaming project from a concept to a live experience isn't just about technical know-how. It requires a thoughtful strategy, realistic goals, and a sharp focus on the person on the other side of the screen. A solid roadmap helps you avoid common headaches and ensures your final product delivers on its promise, both as a business tool and a technical achievement.
The journey starts long before you write any code. First, you need to define what you're building and who it's for. Who is your audience? What devices will they be using—a desktop, a tablet, a phone? Is the goal to sell a product, train a team, or enable collaboration? The answers to these questions will shape every technical choice you make, from the GPUs you select to the network setup you build. This initial planning lays the foundation for a much smoother development process.
Phased Deployment and User Experience
A smart way to begin is with a proof-of-concept (PoC) or a small-scale pilot. This approach minimizes risk and lets you test your core ideas with actual users without a massive budget commitment. A PoC is perfect for validating the user experience and spotting technical hurdles early on, long before you invest in a full-scale deployment. Being honest about timelines and resources at this stage is crucial; a successful pilot makes a powerful case for more significant investment down the road.
Because users are interacting with a live video feed, optimizing their experience is everything. Certain design details become incredibly important:
Graceful Loading States: What does the user see while the server instance is spinning up? A branded loading screen with a progress bar is much better than a blank, unresponsive page.
Managing Expectations: Simple on-screen cues can inform users about their connection quality or potential latency. This small touch can prevent a lot of frustration.
Responsive Interface Design: The user interface (UI) must be built for streaming. Buttons and other elements need to be large enough for touch devices and feel snappy, as if the application were running locally.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Thorough testing is an absolute must for any Unreal Engine pixel streaming application. Your quality assurance (QA) process needs to go beyond standard software testing and concentrate on the unique challenges of a streaming environment. This means benchmarking performance under different network conditions to see how the experience holds up on a spotty connection. It’s also important to have fallback options ready, like automatically lowering the stream resolution or frame rate for users on slower networks.
To help structure this process, here’s a checklist that breaks down the key activities and considerations for each phase of your project.
This table provides a high-level roadmap, but remember to anticipate the unexpected. Robust bandwidth adaptation strategies are essential, allowing the stream quality to adjust automatically without disrupting the user. By planning strategically and testing rigorously, you can deliver a polished, stable, and truly engaging pixel streaming experience that accomplishes exactly what you set out to do.
Your Next Steps: Taking Action Today
The world of Unreal Engine pixel streaming is constantly advancing, bringing new features and possibilities to the table. But this rapid pace shouldn't paralyze you. Instead of waiting for the "perfect" moment, you can take practical steps right now to get your projects running. The key is to start with a clear, manageable goal instead of getting lost in endless planning.
This section provides a straightforward guide for taking your first real steps, whether you're just exploring the technology for a single project or thinking about adopting it more broadly. The best starting point depends entirely on your technical skills and business goals.
Finding Your Starting Point
You don't need to build a custom, from-the-ground-up solution for every project. Your entry into pixel streaming can be scaled to fit your resources and what you want to achieve.
Here are a few ways to begin:
Use a Managed Platform: For teams that want to focus on creating amazing content, not managing servers, a platform-as-a-service (PaaS) is the most direct path. Services like Streampixel handle all the complicated server setup, scaling, and maintenance. You just upload your Unreal Engine application and share a link. This is perfect for getting to market fast with predictable costs.
Run a Local Test: Before you even think about cloud costs, you can test the entire workflow on your own computer. The standard Unreal Engine pixel streaming plugin includes scripts to run a local web server. This is a zero-cost way to understand how the pieces fit together and check your application's performance.
A Practical Evaluation Framework
To figure out if pixel streaming is the right move, ask yourself these essential questions. The answers will become the blueprint for your strategy.
The journey into Unreal Engine pixel streaming isn't an all-or-nothing jump. By starting small, proving your concept, and picking the right path, you can build momentum and show real value quickly.
Ready to see just how easy it can be? With Streampixel, you can deploy your interactive Unreal Engine applications across the globe in minutes, without complex setups or hidden fees. **Get started with Streampixel today** and bring your vision to life.
Article created using *Outrank*

Comments